East London Line
| East London Line | |
|---|---|
 Class 378 train at Whitechapel |
|
| Overview | |
| Type | Suburban rail |
| System | National Rail |
| Status | Operational[1] |
| Locale | Greater London |
| Termini | Highbury & Islington (from 2011) Dalston Junction New Cross Crystal Palace West Croydon |
| Stations | 21 from 23 May 2010; 23 from May 2011 |
| Services | 3 |
| Operation | |
| Opened | 27 April 2010 (preview service)[2] 23 May 2010 (full service)[3] |
| Owner | Network Rail and Transport for London |
| Operator(s) | London Overground |
| Depot(s) | New Cross Gate |
| Rolling stock | Class 378 "Electrostar" |
| Technical | |
| No. of tracks | Double track; sections with four tracks[4] |
| Track gauge | Standard gauge 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) |
| Electrification | 750 V DC third rail |
| London Overground East London Line Extension phase 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The East London line is a London Overground line which runs north to south through the East End and Docklands areas of London. Originally part of the London Underground, the line closed as part of the £1 billion East London line extension in December 2007;[5][6][7] a limited service was introduced on 27 April 2010 and full service began on 23 May 2010.[8] Phase 2, which will link the line to the inner South London Line, is due to be completed before the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Originally built in 1869 by the East London Railway Company, which reused the Thames Tunnel, which had originally been intended for horse-drawn carriages, it became part of the London Underground network in 1933 (coloured orange on the Tube map) before its conversion to overground operation in 2010.
Contents |
History
Establishment of the East London Railway

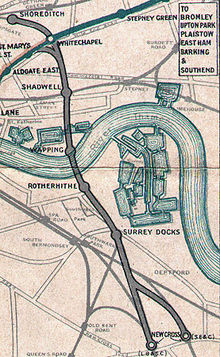
The East London Railway was created by the East London Railway Company, a consortium of six railway companies: the Great Eastern Railway (GER), the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR), the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR), the South Eastern Railway (SER), the Metropolitan Railway, and the Metropolitan District Railway. The latter two operated what are now the Metropolitan, Circle, District and Hammersmith & City lines of the London Underground.
The companies reused the Thames Tunnel, built by Marc and Isambard Kingdom Brunel between 1825 and 1843. The tunnel was built for horse-drawn carriages with generous headroom and two carriageways separated by arches, though it was only used for pedestrian traffic. It connected Wapping on the north bank of the Thames with Rotherhithe on the south bank. A triumph of civil engineering, it was a commercial failure and by the 1860s it had become an unpleasant and disreputable place.
The tunnel was the most easterly land connection between the north and south banks of the Thames. It was close to London's docks on both banks of the river and was not far from mainline railways at either end. Converting the tunnel to a railway thus offered an ideal means of providing a cross-Thames rail link without having to go to the great expense of boring a new tunnel. On 25 September 1865 the East London Railway Company took ownership of the Thames Tunnel at a cost of £800,000.[9] Over the next four years the company built a railway line running through the tunnel to connect with existing railway lines.
The line opened in stages as finance became available:
- 7 December 1869: Initial line from New Cross Gate (then known as New Cross) to Wapping opened, operated by the London, Brighton & South Coast Railway (LB&SCR). Intermediate stations were opened at Deptford Road (now Surrey Quays) and Rotherhithe
- 13 March 1871: A spur was opened from just south of what is now Surrey Quays station to the South London Line's Old Kent Road railway station. Services were withdrawn in 1911 and the track was subsequently removed.
- 19 April 1876: Wapping to Shoreditch opened, running through a cut-and-cover tunnel constructed in part along the bottom of a now infilled dock. At Shoreditch a connection was made with the Great Eastern Railway to Liverpool Street. Intermediate stations were opened at Shadwell and Whitechapel
- 1 April 1880: A spur to New Cross (South Eastern Railway) opened.
- 3 March 1884: A spur linking the Metropolitan and Metropolitan District Railways to the East London Railway opened south of Whitechapel. This enabled Metropolitan Railway and Metropolitan District Railway (District) trains to commence through services to the East London Railway later that year. Although passenger services via this spur ceased in 1941, it was retained to transfer empty trains between the East London line and the rest of the sub-surface network.
Early utilisation
The East London Railway Company owned the infrastructure but it was operated by its controlling railways. Steam trains were initially operated by the GER, LB&SCR and the SER. The LB&SCR used their LBSCR A1 Class Terrier locomotives, which William Stroudley designed partly with this line in mind. It carried both passenger and goods trains; the LB&SCR operated between Liverpool Street and Croydon, the SER introducing a service between Addiscombe and Liverpool Street from April 1880 until March 1884. From March to September 1884 the SER service ran from Addiscombe to St Mary's (MR & MDR Joint Station). Metropolitan Railway services from St Mary's to New Cross (SER) and Metropolitan District Railway services from St Mary's to New Cross Gate (LB&SCR) commenced on 1 October 1884.[10] On 6 October through services started from Hammersmith (Hammersmith & City) to New Cross (SER) and from Hammersmith (MDR) to New Cross (LB&SCR).
Before the development of the Kent coalfields in the early part of the 20th century, house coal from the north for distribution in south London and as far afield as Maidstone and Brighton was an important source of revenue. Access at the north end of the line was difficult: trains were limited to 26 wagons and had to be shunted into the Great Eastern's Liverpool Street station and then drawn forward onto the East London line. From October 1900 additional capacity was offered by a wagon lift, carrying two ten-ton wagons, from the Great Eastern coal depot at Spitalfields to a siding on the ELR near Whitechapel station. The surface junction was taken up in 1966 and the lift closed in 1967, after a fire at the Spitalfields depot.[11][12]
When the Metropolitan District Railway was electrified in 1905 it ceased using the ELR, the last trains running on 31 July 1905;[10] similarly, the Metropolitan Railway suspended its service after 2 December 1906.[10] LB&SCR and GER services continued to run, and SER services recommenced on 3 December 1906.
The line was later electrified, with the controlling railways funding the upgrade and the Metropolitan Railway providing the rolling stock. Electric services began on 31 March 1913 and ran from the two southern termini to Shoreditch and South Kensington via Edgware Road and High Street Kensington. In 1914 the service to South Kensington was diverted to Hammersmith.
After the 1923 Grouping the goods service was operated by London and North Eastern Railway (as successors to the GER), with the Metropolitan Railway continuing to provide passenger services.
The London Underground era

Wapping station on the East London line, built into the original northern entrance shaft of the Thames Tunnel. The station was rebuilt in the early 1980s.

The link to Liverpool Street, 1991
A dilapidated, graffiti-strewn Shoreditch tube station in December 2007. It closed on 9 June 2006 after 93 years of Underground service.

A train of A stock stands at Surrey Quays
|
| East London line (pre-conversion) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| {{{Logo}}} | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Colour on map | Dark Orange | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year opened | 1869 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line type | Sub-Surface | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rolling stock | A Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stations served | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Length | {{{Length}}} | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depots | New Cross Neasden |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Journeys made | 10,702,000[6] (per annum) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Rail lines of Transport for London
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 1933 the East London Railway came under the control of the London Passenger Transport Board. Although the infrastructure was still privately owned, passenger services along the line were operated under the auspices of the "East London Branch" of the Metropolitan Line. In 1948 the railways were nationalised and became part of the newly created British Transport Commission along with the Underground. Goods services continued to use the line until 1962, occasional passenger trains from Liverpool Street until 1966. The short length of track connecting Shoreditch to Liverpool St was removed in 1966. The service to Shoreditch was also reduced, with Whitechapel becoming the northern terminus for much of the time; by the time Shoreditch station closed in 2006, it was open at peak times on weekdays and most of Sundays (for Brick Lane Market), and closed on Saturdays.
Westbound services were steadily curtailed during the early part of the Underground era. The service to Hammersmith was reduced to peak hours only in 1936 and was withdrawn altogether in 1941, leaving the East London branch as an isolated appendage on the edge of the Underground network. Its only passenger interchange to the Underground was at Whitechapel, with interchanges to main line trains at the two New Cross stations. In the 1980s and 1990s the line gained two important new connections: Shadwell became an interchange with the Docklands Light Railway in 1987, and a new station was added at Canada Water in 1999 for interchange with the then new Jubilee Line extension.
The identity of the East London line changed considerably during the London Underground era. On Tube maps between 1933 and 1968 it was depicted in the same colour as the Metropolitan line. In 1970 it was renamed the "Metropolitan Line - East London Section", in Metropolitan line purple with a white stripe down the middle. In the 1980s it was renamed as a line in its own right (though it was still grouped operationally with the Metropolitan line) and from 1990 the colour changed to orange.
The maintenance of the line passed to the Metronet consortium in 2003 under a Public-Private Partnership, although the operation of trains continued to be the responsibility of TfL.
According to TfL, the line carried 10.7 million passengers per year before its temporary closure in 2007.[6]
Physical characteristics
The East London Line was the only Underground line not to penetrate Travelcard Zone 1. It was the second shortest line (after the Waterloo & City Line), with an end-to-end journey time of 14 minutes. Its length was 9 km (5 miles), with nine stations. At the time of its closure in 2007 it ran in a continuous tunnel from Whitechapel to Surrey Quays, with the remainder on the surface or in cutting. Much of the line was built as cut-and-cover. The deepest point is at Wapping station, constructed in the Thames Tunnel's original entrance shaft 18.29 m (60 ft) below the surface.[6]
At time of closure, the line connected with Southeastern mainline services at New Cross and Southern at New Cross Gate. Underground connections were at Canada Water (Jubilee line) and Whitechapel (District and Hammersmith & City Lines). A non-contiguous connection with the Docklands Light Railway was at Shadwell, with a separate DLR station some 50 m (150 ft) away. Although the interchange was via the street, through ticketing was permitted at time of closure in 2007.
A link with the Metropolitan and District lines was made just south of Whitechapel via St Mary's Curve. This has been out of passenger use since 1941 but was still used to transfer rolling stock to and from the Metropolitan line's main depot at Neasden. The curve can easily be seen on the northbound and eastbound approaches to Whitechapel station, although a temporary wall was built across the line in January 2008, close to the junction with the District line.
Most of the line was double-tracked, with Shoreditch station and the final sections into the southern termini single-tracked, the latter because of lack of space. This required southbound trains to alternate between the two termini.
Rolling stock
The East London line used Metropolitan Line A60 and A62 sub-surface rolling stock manufactured by Cravens of Sheffield in two batches between 1960 and 1962. It was upgraded in 1994 with improved suspension, lighting, heating and ventilation. The rolling stock was regularly interchanged with that used on the main Metropolitan line and usually carried both East London and Metropolitan line maps. However, the trains used on the ELL were always double ended four car units. (This means that there was a fully operational driving cab at each end, unlike the Metropolitan line trains that, aside from the Chesham shuttle, run as eight-car trains with no o.p.o. facilities in the middle cabs, making them effectively single-ended units for service work. The trains operating on the Met. main line were mostly comprised of two single-ended units coupled together with fully operational driving cabs at each end. Therefore they could use any ELL trains, but the ELL could only use the double-ended units converted for their use.)
Seven four-car trains operated the line (six off-peak, seven during peak hours when Shoreditch was open). During off-peak times, train 7 became the spare. The line operated some of the shortest trains on the network, necessitated by short platforms. The small number of trains made the line particularly sensitive to disruption caused by vandalism, train faults or staff shortages. Sometimes in the early 2000s only two trains were running. The withdrawal of a single train amounted to a 17% cut in capacity — the Metropolitan line would have to lose nine trains to suffer the same percentage cut. Trains were operated by just a driver: the decision to withdraw the guards prompted an unsuccessful strike by the National Union of Railwaymen in May 1985.[13]
Light maintenance and stabling took place at a small depot near New Cross, with heavier work at the main Metropolitan line depot at Neasden. Between 1985 and 1987, D78 stock operated the line before being replaced by A60 and A62 stock. During the 1970s the line was operated by 1938 Tube stock.
Stations
The London underground period stations in order from north to south were as follows:
- Shoreditch - opened 10 April 1876, first Underground service 31 March 1913, closed 9 June 2006. Only station not to be reopened in 2010 (replaced by Shoreditch High Street).
- Whitechapel - ELR station opened 10 April 1876, first Underground service at ELR platforms 31 March 1913. Interchange with District and Hammersmith & City Lines.
- Shadwell - opened 10 April 1876, first Underground service 1 October 1884. Interchange with Docklands Light Railway.
- Wapping - opened 7 December 1869, first Underground service1 October 1884.
- Rotherhithe - opened 7 December 1869, first Underground service 1 October 1884.
- Canada Water
 - opened 17 September 1999. Interchange with Jubilee Line.
- opened 17 September 1999. Interchange with Jubilee Line. - Surrey Quays - opened as Deptford Road 7 December 1869, first Underground service 1 October 1884, renamed Surrey Docks in 1911.
- line splits
- New Cross Gate - ELL platform opened 7 December 1869, first Underground service 1 October 1884. Interchange with Southern mainline services (mainline station was opened as New Cross in 1839, and renamed 1923).
- New Cross
 - ELL platform opened 1 April 1880, first Underground service 1 October 1884. Interchange with Southeastern mainline services (mainline station was opened in 1850).
- ELL platform opened 1 April 1880, first Underground service 1 October 1884. Interchange with Southeastern mainline services (mainline station was opened in 1850).
Conversion to overground rail operation
Engineering work on the East London line extension started in 2005 and the existing underground service ended in December 2007.
Between 2007 and May 2010 London Buses route ELW Whitechapel - Shadwell - Wapping (every 10 minutes, evenings & weekends 15 minutes) was in service. Starting on 23 December 2007 it was extended from Whitechapel to Shoreditch (Monday-Friday 0700-1030 & 1530-2030, Sunday 0700-1530) from 19 July 2008. It was reduced to weekends only from 28 April 2010 and withdrawn on 9 May 2010.
Between 2006 and May 2008 a number of other rail replacement buses were provided. ELS Whitechapel - Shoreditch (Monday-Friday 0700-1030 & 1530-2030, Sunday 0700-1530 commenced 10 June 2006 and was withdrawn on 19 July 2008 (replaced by a peak hour extension of route ELW). ELC New Cross Gate - New Cross - Surrey Quays - Canada Water (Monday-Friday every 5–10 minutes, weekends every 15 minutes) commenced 23 December 2007 and was withdrawn on 26 September 2009 due to lack of use. ELP Canada Water - Rotherhithe (every 15 minutes) began on 23 December 2007 and was withdrawn on 24 February 2008 due to lack of use: tickets were valid between Bermondsey and Canada Water on standard route 381.
Recent developments
East London Line extension - phase 1
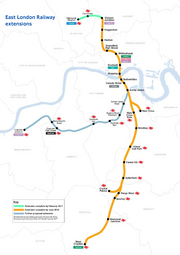
The former underground line was extended northwards from Whitechapel, with new stations at Shoreditch High Street, Hoxton, Haggerston and Dalston Junction using 3.6 km of new trackbed between Whitechapel and the Broad Street viaduct and existing disused trackbeds for most of the distance. A further extension to Highbury & Islington is expected to be completed in 2011.
It was also extended south to connect to the London Bridge arm of the Brighton Main Line, linked via a northbound flyover north of New Cross Gate. Other than the new flyover and some associated works around New Cross Gate, it will use almost entirely existing tracks, with services running south to West Croydon via Brockley, Honor Oak Park, Forest Hill, Sydenham, Penge West, Crystal Palace (by way of a branch), Anerley and Norwood Junction. No new stations have been constructed on this section.
The official opening of the majority of phase 1 of the East London line extension took place on 23 May 2010. Use of the line is expected to increase from the previous 10.4 million passengers per year to 35.4 million, and to 50 million when phase 2 is finished.[14] 23 new four-car Bombardier units were provided as well as 25 dual-voltage three-car units for the North London Line. These areClass 378 Capitalstar trains.
The existing track and the northern extension remain under TfL ownership, and the stations from Dalston Junction to Surrey Quays are part of the London Overground network.[15] The extension will run northwards from Whitechapel to Dalston Junction, and south to Crystal Palace and West Croydon.
Current developments
Highbury & Islington extension
The line will be extended northwards to Highbury & Islington by May 2011. [16]
East London line extension phase 2
A 2.5 km link is planned as part of the East London line extension running from south of Surrey Quays to the Network Rail Inner South London Line to Clapham Junction, by way of Queens Road Peckham, Peckham Rye, Denmark Hill, Clapham High Street and Wandsworth Road. Work is scheduled for completion by May 2012 [17] in time for the 2012 Olympics.[18] A new station at Surrey Canal Road was also planned, but this was put on hold in 2009.[19]
The extension will use an alignment between Rotherhithe and Peckham which has been disused since 1911 via the now defunct Old Kent Road station.
Gallery
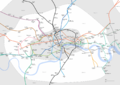 A geographically accurate map of zones 1 and 2 of the Underground, showing the London underground era East London line (towards the right-hand side of the map) |
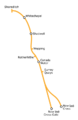 Geographically accurate map showing the London Underground period East London line |
East London Line Rail Replacement Bus services advertisement |
External links
- East London line - London Underground website
- East London line Project (official home page)
- East London line extensions map
- Official suspension notice
- Video Flyover of Phase 1
References
- ↑ "Dalston Junction to West Croydon". Transport for London. 23 May 2010. http://www.tfl.gov.uk/corporate/projectsandschemes/15360.aspx. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- ↑ "East London Line officially opened by Boris Johnson". BBC News Online (London). 27 April 2010. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/london/8620188.stm. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Clarke, Megan (21 April 2010). "Party Time for East London Line". London Evening Standard (London). http://www.thisislondon.co.uk/standard/article-23826543-party-time-for-east-london-line.do. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Even though this would more correctly be 2 for the ELL and a further 2 for the North London Line
- ↑ "East London Line alternative transport strategy update". London Underground. 27 November 2006. http://www.gold.ac.uk/east-london.pdf. Retrieved 24 December 2006.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 East London line facts, Transport for London.
- ↑ "First train runs on East London Railway". Railnews. 8 October 2009. http://www.railnews.co.uk/news/metro/2009/10/08-first-train-runs-on-east.html. Retrieved 8 October 2009.
- ↑ "Full service begins on newly extended East London Line". BBC News Online (London). 23 May 2010. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/london/8699262.stm. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- ↑ "Railway And Other Companies, East London". The Times (London). 2 September 1869.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Rose, Douglas (December 2007) [1980]. The London Underground: A Diagrammatic History (8th ed.). Harrow Weald: Capital Transport. ISBN 978-1-85414-315-0.
- ↑ Gordon, W.J. (1910). Our Home Railways (volume one). London: Frederick Warne. p. 153.
- ↑ Klapper, Charles (1976). London’s Lost Railways. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul. pp. 94–98. ISBN 0-7100-8378-5.
- ↑ "Illegal subway strike called off in London". Globe & Mail (Toronto). 21 May 1985.
- ↑ Greater London Authority (16 November 2004). "London takes over responsibility for building East London line extension". Press release. http://www.london.gov.uk/view_press_release.jsp?releaseid=4547.
- ↑ London Overground signs standard.
- ↑ "Hughbury & Islington extension in May 2011". Transport for London. http://www.tfl.gov.uk/corporate/projectsandschemes/15360.aspx.
- ↑ [Rail Express issue 154 March 2009]
- ↑ "London rail link gets green light". BBC News Online (London). 12 February 2009. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/london/7886008.stm. Retrieved 16 February 2009.
- ↑ McKenna, John (12 February 2009). "East London Line extension to Clapham to be built by London 2012". New Civil Engineer. http://www.nce.co.uk/news/2009/02/east_london_line_extension_to_clapham_to_be_built_by_london_2012.html. Retrieved 16 February 2009.
Various sources have been used in the creation of this article, including the external links above, email conversations with the ELL Project Team and emails from the ELL Project Team update newsletter.
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||